What Is AI Art? How Artificial Intelligence Is Changing Contemporary Art



What Is AI Art? How Artificial Intelligence Is Changing Contemporary Art
AI art combines human input with machine algorithms to create visual works. Artists provide instructions (like prompts or parameters), and AI tools generate the output, ranging from abstract designs to realistic portraits. This emerging field is reshaping art creation, distribution, and ownership. Key points:
- How It Works: AI uses techniques like GANs and text-to-image models to produce art. Artists guide the process but rely on AI for execution.
- Notable Sales: Portrait of Edmond de Belamy sold for $432,500 in 2018, and Dmitri Cherniak's Ringers #879 fetched $6.2 million in 2022.
- Creation Process: Choose an AI tool (e.g., DALL-E, Midjourney), craft detailed prompts, and refine results for the best output.
- Market Impact: Platforms like Art Blocks enable artists to sell AI-generated works as NFTs, offering new earning opportunities.
- Challenges: Copyright issues, ethical concerns, and debates about authorship and creativity remain unresolved.
AI art is influencing how art is made, sold, and perceived, while raising questions about the role of technology in creative expression.
AI art, explained
sbb-itb-4e84554
What Is AI Art?
AI art is the result of combining human creativity with the computational power of algorithms. In this process, the artist sets the parameters and provides prompts, while the AI takes over to generate the artwork. The outcomes range from abstract designs to hyper-realistic portraits. This collaboration between human direction and machine learning gives AI art a distinct identity compared to traditional digital tools.
The Definition of AI Art
What sets AI art apart from traditional digital art is autonomy. When using tools like Photoshop or Procreate, the artist meticulously controls every brushstroke and color choice. In contrast, AI art relies on algorithms to make decisions about visual elements. These algorithms learn patterns from massive datasets, allowing them to autonomously generate details once the artist initiates the process.
This places AI art within the broader realm of generative art, which refers to works created by systems with a degree of independence. Earlier forms of generative art depended on explicit coding or random elements, like rolling dice. Modern AI art, however, uses machine learning to establish its own parameters, producing outputs that are often more varied and unpredictable.
Understanding this distinction helps underscore the unique technological foundation of AI art.
Technologies That Power AI Art
AI art relies on advanced machine learning techniques to bring creative visions to life. Some of the most notable technologies include:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These involve two neural networks - a generator that creates images and a discriminator that evaluates them. The networks work in tandem, refining the output until the generated images resemble human-made art.
- Text-to-Image Models: Tools like DALL-E and Midjourney use transformer architectures to turn written descriptions into visual representations, bridging language and imagery.
- Neural Style Transfer: This technique extracts the artistic style of one image (like Van Gogh’s brushwork) and applies it to the content of another image, creating a hybrid piece.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): These introduce randomness into the creative process, enabling the generation of unique and diverse variations in artwork.
Each of these technologies plays a role in shaping the possibilities of AI-generated art.
Examples of AI-Generated Art
AI art has already made waves in the art world, capturing attention and commanding high prices. In October 2018, the collective Obvious sold Portrait of Edmond de Belamy at Christie's New York for an impressive $432,500. In 2022, artist Refik Anadol presented Unsupervised at the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA). This installation used a custom AI model trained on 200 years of MoMA’s collection - about 138,000 records - to create continuously evolving abstract visuals displayed on a massive digital screen.
Another notable example is Dmitri Cherniak’s Ringers #879, often called "The Goose", which sold for $6.2 million at Sotheby’s. These examples highlight the growing appeal and market value of AI-driven art.
How to Create AI Art: Step-by-Step
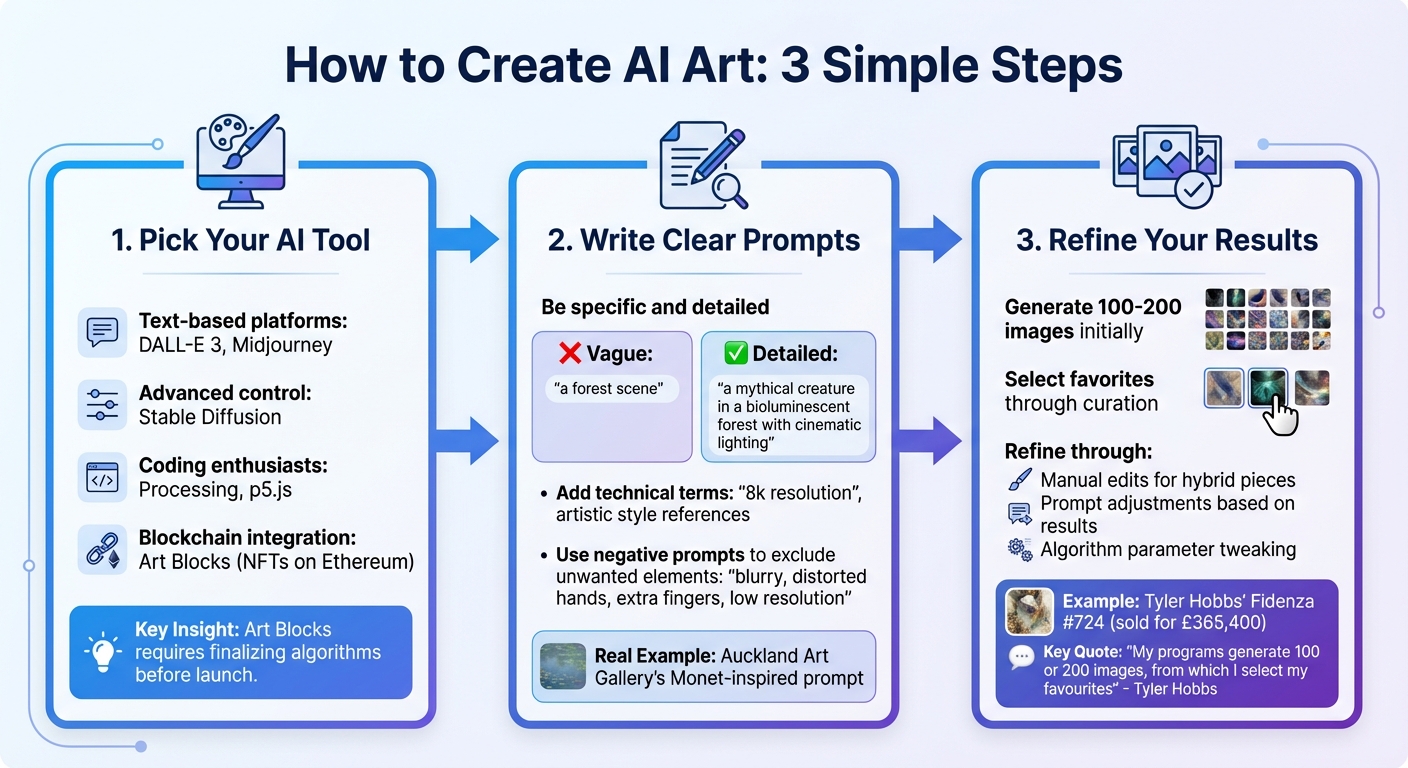
How to Create AI Art in 3 Steps: Tool Selection, Prompt Writing, and Refinement
You don’t need to be a tech wizard to dive into the world of AI art. The process boils down to three straightforward steps: picking the right tool, crafting effective prompts, and fine-tuning the results. This approach keeps you in the driver’s seat while letting AI handle the heavy lifting.
Step 1: Pick Your AI Tool
Start by selecting an AI tool that matches both your comfort level and artistic vision. For text-based creations, platforms like DALL-E 3 or Midjourney are great choices. If you want more control or value privacy, Stable Diffusion is worth exploring.
For those who enjoy coding, tools like Processing and p5.js allow you to create custom algorithms for geometric or pattern-based designs. If you’re interested in blending generative art with blockchain technology, Art Blocks is an exciting option. This platform hosts your generative code on the Ethereum blockchain, turning each piece into a unique NFT. When Erick "Snowfro" Calderon founded Art Blocks in 2020, he introduced a unique challenge: artists had to finalize their algorithms before launch, ensuring every possible output met their creative standards.
Step 2: Write Clear Prompts
Think of prompts as the instructions you give the AI - it’s your way of directing its creativity. The more detailed and specific you are, the better the outcome. For example, instead of saying "a forest scene", try something like "a mythical creature in a bioluminescent forest with cinematic lighting". Including technical terms like "8k resolution" or referencing specific artistic styles can further refine the AI’s output.
Auckland Art Gallery showcased this in 2024 by using DALL-E with the prompt:
"An impressionist-style painting with extremely loose expressive brushstrokes inspired by Monet's water garden."
The result captured Monet's signature color palette and brushwork. You can also use negative prompts to exclude unwanted elements like "blurry, distorted hands, extra fingers, low resolution" - a handy trick for improving the quality of your images.
Step 3: Refine Your Results
Creating standout AI art often involves generating a large batch of images - sometimes 100 to 200 - before zeroing in on the best ones. Generative artist Tyler Hobbs explains:
"My programs are varied because of the randomness that I carefully build into them. They often generate 100 or 200 images, from which I select my favourites."
Once you’ve chosen your top picks, you can refine them further. For hybrid pieces, manual edits can add a personal touch. For instance, Hobbs used a plotter to transfer his AI-generated work, Fidenza #724, onto paper, then enhanced it with gouache to create texture and depth. This piece later sold for £365,400 at Christie's London in February 2023.
If you’re sticking to digital art, you can tweak your prompts based on initial results or adjust the algorithm’s parameters to produce more targeted outputs. This editing process - where you act as both creator and curator - is what transforms raw AI outputs into polished, meaningful artwork. By following these steps, you can guide the creative process while tapping into AI’s powerful capabilities.
Why Artists Are Using AI in Contemporary Art
Artists are embracing AI not to replace their creativity, but to push its boundaries. This technology acts as a collaborator, helping them work faster, experiment with new styles, and tap into revenue opportunities that didn’t exist just a few years ago.
Faster Art Production
AI dramatically speeds up the creative process by reducing the time it takes to visualize ideas and explore variations. What used to take hours or even days can now be done in minutes. Tyler Calkin, Associate Professor of Art at the University of Nevada, Reno, puts it this way:
"helpful for rapid visualization in the creative process, effectively acting as a time-saving tool by increasing the number of variations or iterations an artist might make anyway".
Chinese artist Miao Xiaochun captures the sentiment more succinctly:
"The new technology gives me four hands".
A 2024 study focusing on contemporary artists and professionals in China found that 87.5% of them incorporate AI into their work. Beyond visual creation, tools like ChatGPT are helping artists overcome technical challenges in seconds - tasks that once required hours of effort.
New Styles and Creative Options
AI is unlocking possibilities for blending artistic styles from different eras or creating visuals that would be nearly impossible to achieve manually. A standout example is Refik Anadol’s 2022 project "Unsupervised" at the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA). By training a custom AI model on 200 years of MoMA’s internal data, Anadol generated abstract, real-time digital artworks that combined historical art movements into entirely new forms.
AI also plays a key role in post-photography, a practice that merges analog and digital techniques to challenge traditional visuals. Massive datasets - ranging from museum archives to climate data and even social media sentiment - are being used by artists to craft data-driven narratives that push the boundaries of what art can be.
Market Demand and Revenue Options
AI art isn’t just transforming creativity - it’s reshaping the business of art. New revenue streams have emerged, fueled by the growing demand for AI-generated works. In May 2022, Refik Anadol’s NFT "Living Architecture: Casa Batlló" sold for an impressive $1,380,000 at Christie's.
Platforms like Art Blocks are giving artists a way to host their algorithms on the Ethereum blockchain, allowing buyers to mint unique iterations of their projects. Artists are also meeting collector demand for physical-digital hybrids by pairing NFTs with tangible items like plotter drawings or prints. Additionally, platforms like Twitter and Discord are becoming vital spaces for artists to connect directly with their audience, build buzz, and sell their work.
Pros and Cons of AI Art
AI art brings both exciting opportunities and notable challenges for artists and collectors alike. Here's a closer look at the benefits and concerns surrounding the integration of AI into the art world.
Benefits of AI Art
AI tools have made creating art more accessible than ever, removing many of the technical barriers that once excluded aspiring creators. This shift allows individuals who might have felt disconnected from the art world to participate and express themselves.
The technology also supports the emergence of new artistic styles. For example, "post-photography" merges the boundaries between the real and the virtual, while "emergent" art lets autonomous systems independently determine creative features.
The market potential for AI art is immense. Blockchain platforms offer secure ways for artists to sell digital works and connect with collectors globally. Additionally, social platforms like Discord and Twitter enable creators to interact directly with their audiences, gaining real-time feedback and building value through community engagement.
Challenges of AI Art
One of the most pressing issues with AI art is copyright and ownership. It remains unclear whether the rights to AI-generated works belong to the artist, the developer of the AI tool, or if such works can even be copyrighted at all. This uncertainty creates risks for both creators and buyers.
Another challenge lies in the perception of AI-generated art. Studies show that when people know a piece was created by AI, they often rate it lower in emotional depth and craftsmanship. Art historian Drimmer critiques AI art, stating:
"AI-generated art fails to promote knowledge growth... it does not provide insights into the functions of art, the intentions of artists, or their creative processes".
There are also ethical concerns tied to how AI systems are trained. Critics argue that these systems often use artists' works without their consent or compensation, a practice some refer to as "labor theft". Additionally, biases in training data can result in outputs that lack inclusivity or reflect existing prejudices.
While AI art offers exciting new possibilities, these challenges highlight the need for careful consideration and solutions.
Comparison: AI Art Benefits vs. Challenges
| Category | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Artist Impact | Faster creation; greater accessibility for new creators; expanded options | Risk of replacing traditional techniques; reduced emphasis on human creativity |
| Market Value | Successful auctions; new revenue streams through NFTs and blockchain | Oversaturation of the market; potential devaluation if viewed as overly mechanical |
| Ethics & Integrity | Democratized access to art; transparency via blockchain-stored code | Copyright issues; concerns over labor theft; algorithmic bias in training data |
Key Takeaways
AI Art Is Changing How We Create
AI has become a creative partner for artists, blending human vision with machine precision. While artists set the vision and parameters, AI handles the technical execution, opening doors to styles and outcomes that were once out of reach. A key element of this shift is creative coding, where artists write programs to generate numerous unique pieces instead of crafting just one static artwork. Even the collector's role has evolved. In on-chain generative art, collectors actively participate by triggering the final creation of a piece at the moment they purchase it, giving them a hands-on role in the creative process. These developments are encouraging artists to explore and engage with AI in thoughtful and meaningful ways.
Getting Started with AI Art
For newcomers, platforms like Midjourney, DALL-E, or Artbreeder offer an easy entry point. For those seeking more control, learning creative coding languages such as Python, JavaScript, or Processing can open up advanced possibilities. Blockchain platforms like Art Blocks provide a way to secure and sell your creations as NFTs. Additionally, digital artists can bypass traditional gatekeepers by connecting directly with fans and buyers on platforms like Twitter and Discord.
Using AI Art Responsibly
Transparency is key when working with AI. Clearly communicate AI's role in your creative process to address ethical concerns and set realistic expectations for your audience. Major challenges include the unconsented use of artists’ data and algorithmic bias. To preserve your unique artistic voice, refine and edit AI-generated outputs. Use tools that safeguard intellectual property and ensure training data is used with proper consent.
FAQs
How is AI art different from traditional digital art?
AI-generated art emerges from algorithms that process massive datasets to create visual content, drawing on patterns they've learned. While artists play a crucial role in this process - choosing styles, subjects, or color schemes - the AI takes over to fill in the finer details. This often leads to surprising and imaginative outcomes that blend human direction with machine ingenuity.
On the other hand, traditional digital art is entirely shaped by the artist's hands. Programs like Photoshop or Illustrator serve as tools, but every stroke, line, and detail is meticulously crafted by the creator. Unlike AI art, which thrives on collaboration between human and machine, traditional digital art is a purely human-driven endeavor, reflecting the artist's vision without algorithmic influence.
What ethical concerns come with AI-generated art?
AI-generated art brings a host of ethical challenges that ripple through the world of artists, collectors, and the larger art community. One of the biggest concerns revolves around copyright and originality. Many AI models are trained on massive collections of existing artwork - often without the original artists' permission. This raises thorny questions about uncredited use of copyrighted material and who actually owns the rights to the final creation.
Another pressing issue is bias and harmful content. Since AI systems learn from the data they're fed, they can unintentionally mirror societal biases embedded in that data. This can lead to outputs that are offensive or reinforce stereotypes. On top of that, privacy concerns come into play when AI recreates recognizable faces or personal details without consent, blurring the line between creative expression and misinformation.
Finally, there's the worry about the impact on creative jobs. As AI tools grow more sophisticated, some fear they could edge out illustrators, photographers, and other visual artists, sparking debates about the role of human creativity in an increasingly tech-driven art world.
These challenges underscore the importance of using AI responsibly in the art industry, ensuring fairness, transparency, and respect for the people behind the creativity.
How can artists protect their AI-generated art legally?
Artists looking to legally protect their AI-generated artwork can take a few key steps. First, make sure your work meets the requirements for copyright protection by showing there was human creativity involved in its creation - copyright laws generally hinge on this human contribution. Second, use licensing agreements to spell out exactly how others are allowed to use your art. Lastly, working with an intellectual property attorney can be invaluable for navigating the often tricky legal issues surrounding AI tools and ownership rights.
Although laws regarding AI-generated art are still developing, taking these steps can help you protect your work and establish clear rights over your creations.



